| Re: Crossover Answer [message #73614 is a reply to message #73613] |
Sat, 18 August 2012 13:58   |
 |
 Wayne Parham
Wayne Parham
Messages: 19003
Registered: January 2001
|
Illuminati (33rd Degree) |
|
|
That's right, exactly. Manipulation of the values (or the load) changes the transfer function and phase. You can slightly overdamp or underdamp the filter to provide a little bit of a peak or dip at the crossover frequency, and do other little adjustments like that.
I don't know of any optimized crossover that uses textbook values because it is useful to dial-in the transfer function and phase by modifying the values a little bit. You can do this by trial-and-error (solder/measure) or you can use Spice to model the circuit, to get it close first.
I prefer a combined approach, possible with the Smith & Larson WTPro system. It allows me to essentially build an active crossover using properties configured by a Spice model. I can change crossover values just by typing them into the Spice model. Once the crossover is perfected, I can build a physical model and it measures exactly like the simulated one did. It's really a very useful tool.
All you have to do is to measure the drivers impedance, and type up a Spice (nodelist) model. Spice is kind of cumbersome at first, I suppose, but I've been doing it so long it seems very natural to me. But crossovers are pretty simple circuits, so they're easy to model in Spice. You may already have experience with it modeling tube amps, and if so, this is cake to you.
Once you have the Spice model and the driver impedance measurements, you run the ICD in WTPro. It sends test signals out to the right and left outputs, which you run through amps to the woofer and tweeter. Set the microphone out in front of the speaker, wherever you want to measure from. The WTPro becomes active crossover and test platform, providing acoustic measurements of the loudspeaker using the crossover defined in the Spice model.
Here's a writeup of how I do that when I design a loudspeaker. There's even a video showing me testing for the position of the vertical nulls, which I set by adjusting the crossover values in my Spice model. I can get them to be precisely where I want them to be using this approach.
When the loudspeaker design is fully optimized, this is an example of the (amplitude and phase) response I get:
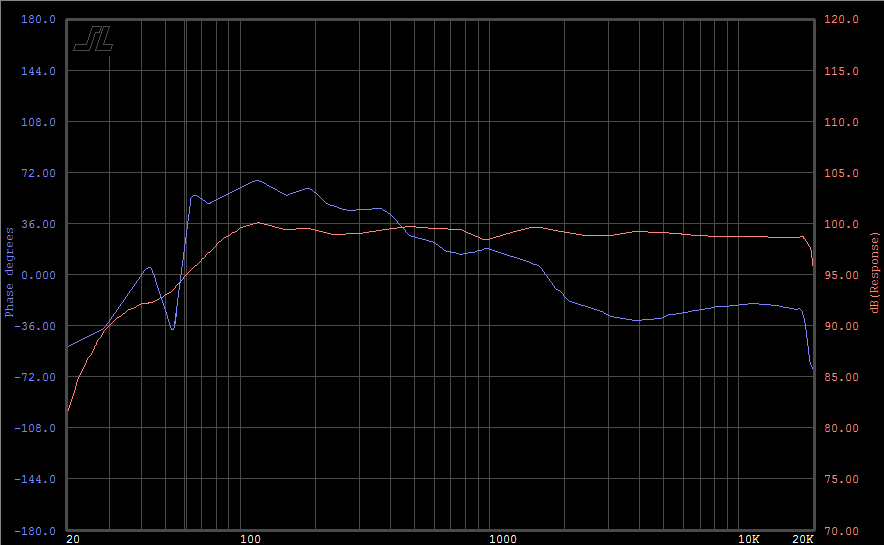 four π loudspeaker amplitude and phase response
four π loudspeaker amplitude and phase response
|
|
|
|